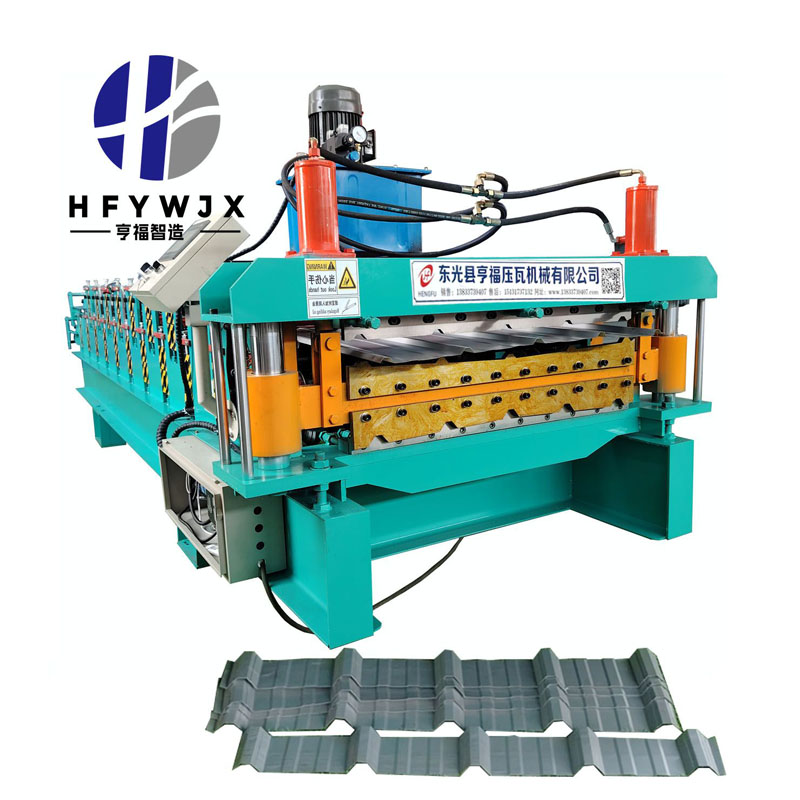
Choosing the Right Roller Material for Double Layer Roll Forming
writer:优化 release time:2025-11-17 20:44:57 Views:51frequency
For any metal forming factory operating a Double Layer Roll Forming Machine, the roller material is one of the most influential factors in determining forming accuracy, surface finish, and long-term production stability. As a professional manufacturer with strong in-house production capacity, the quality of roller materials not only affects machine reliability but also directly impacts your ability to deliver consistent output for large projects and bulk industrial supply.
Selecting the correct roller material ensures the equipment maintains precision, resists wear, and handles the operational demands of dual-profile forming.
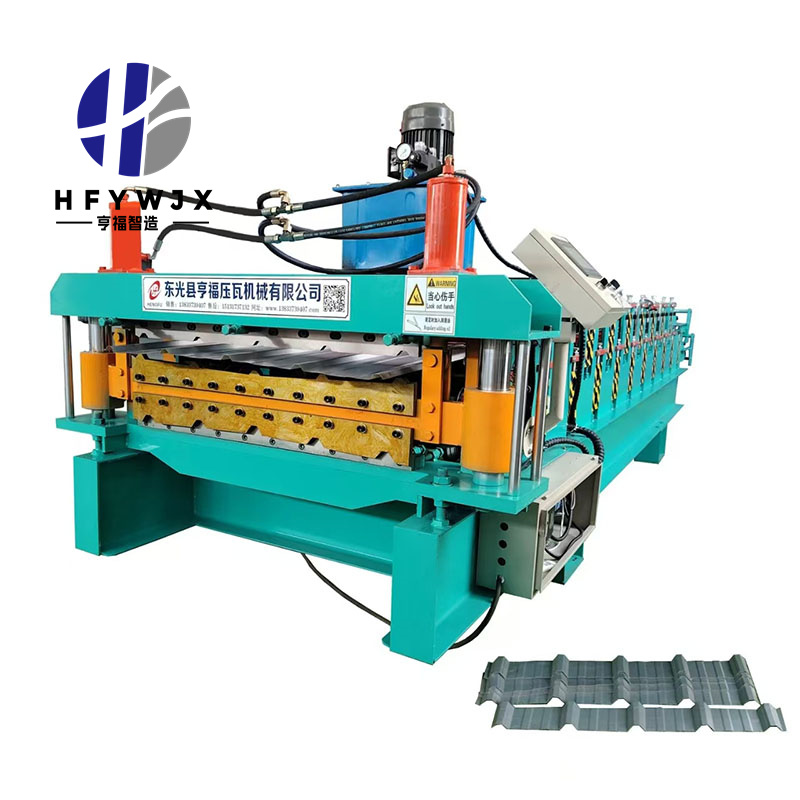


Why Roller Material Matters in Double Layer Forming
In a double-layer forming system, the rollers must shape two different panel profiles within a shared structure. This introduces unique stresses such as:
·Different loading forces between upper and lower layers
·Rapid profile switching
·Continuous operation at mid-to-high line speeds
·Varying metal sheet hardness and thickness
When roller materials are not optimized for these conditions, operators may encounter:
·Uneven profile geometry
·Surface scratching on sheets
·Excessive wear on forming stations
·Vibration increases during high-speed runs
·Higher maintenance demands
Choosing the appropriate roller material is essential for achieving stable forming quality and reducing operational costs over time.
Common Roller Material Options
1. Alloy Tool Steel (Such as GCr15 or Cr12MoV)
Alloy tool steels have become the standard choice for most roll forming applications. After precise heat treatment, they exhibit high hardness and wear resistance, allowing them to maintain shape even during extended production cycles.
These materials are particularly suitable for forming galvanized steel and mild steel sheets, which are commonly used in roofing and wall panels.
Strengths:
·High hardness and durability
·Good wear resistance
·Stable performance under long-term production
Limitations:
·Improper heat treatment may reduce service life
·Not ideal for extremely delicate surfaces
2. 42CrMo High-Toughness Steel
42CrMo offers excellent strength and shock resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty forming environments. Its rigidity helps maintain precise roller contours, especially in production lines that handle thicker or harder sheet materials.
This material appeals to manufacturers who need reliable, long-lasting rollers and who operate their Double Layer Roll Forming Machine in demanding industrial settings.
Advantages:
·Strong impact resistance
·High load-bearing capability
·Excellent dimensional stability
3. Stainless Steel Rollers
Stainless steel is especially popular in environments exposed to humidity, corrosion, or long storage intervals. It helps preserve roller surface quality and prevents rust from affecting forming accuracy.
Stainless steel is also preferred when forming pre-painted color sheets or coated metals that require extremely smooth, scratch-free contact.
Advantages:
·Superior corrosion resistance
·Protects delicate sheet surfaces
·Minimizes risk of scratching
Disadvantages:
·Higher cost
·Lower hardness compared to hardened steels
4. Tungsten Carbide–Coated Rollers
For factories pushing high-speed production or long continuous runs, tungsten carbide coating offers exceptional surface hardness and durability. It significantly reduces wear and helps sustain precise forming dimensions even under challenging conditions.
Carbide coating is often used in premium production lines where downtime must be minimized.
Key Benefits:
·Outstanding wear resistance
·Very high surface hardness
·Consistent forming accuracy
How to Choose the Proper Roller Material
1. Evaluate the Type of Sheet Material
The sheet material used in your project directly influences roller selection:
·If forming galvanized or mild steel → use hardened alloy steel
·If forming pre-painted or coated sheets → use stainless steel or carbide-coated rollers to avoid surface damage
·If forming thicker or high-strength sheets → select 42CrMo for stability
2. Consider Your Production Volume and Speed
Higher speeds and longer shifts place greater demands on rollers.
For large-scale manufacturers with continuous production requirements, choose materials designed for extended endurance, such as:
·Heat-treated alloy steel
·Tungsten carbide–coated rollers for intensive daily output
These choices help maintain profile accuracy and lower maintenance frequency.
3. Pay Attention to Maintenance Expectations
In double-layer systems, roller alignment is essential for forming consistency. Choosing materials that resist deformation, especially 42CrMo and tungsten carbide, can greatly reduce the need for frequent adjustments.
When roller surfaces remain stable, the machine produces uniform profiles and maintains long-term forming accuracy.
4. Balance Long-Term Value With Initial Cost
While basic alloy steels provide a cost-effective solution, higher-grade materials offer extended roller life and more stable performance. Stainless steel and carbide-coated rollers require a higher initial investment but may deliver lower lifetime costs through reduced wear and fewer replacements.
The best option depends on the production environment, expected service life, and the types of panels being manufactured.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct roller material is a critical factor in ensuring the smooth operation, accuracy, and output quality of any Double Layer Roll Forming Machine. Roller materials directly influence forming precision, surface quality, and overall machine durability.
For manufacturers with strong production capacity and large-scale supply requirements, selecting roller materials that align with sheet type, forming pressure, and operational intensity ensures reliable, long-term performance.
By choosing durable, stable, and well-suited roller materials, you can significantly improve forming efficiency, reduce maintenance, and support consistent high-volume output across diverse building panel applications.
References
GB/T 7714:Hosford W F, Caddell R M. Metal forming: mechanics and metallurgy[M]. Cambridge university press, 2011.
MLA:Hosford, William F., and Robert M. Caddell. Metal forming: mechanics and metallurgy. Cambridge university press, 2011.
APA:Hosford, W. F., & Caddell, R. M. (2011). Metal forming: mechanics and metallurgy. Cambridge university press.