Metal Roof Machine Electrical System Maintenance Tips
writer:优化 release time:2025-12-06 11:58:20 Views:188frequency
For manufacturers operating high-throughput sheet-metal forming lines, a Metal Roof Machine supplied by a dependable manufacturer with consistent production capability and reliable bulk-supply support is an essential component of daily fabrication work. Even though the mechanical structure is designed for endurance, the electrical system determines whether the machine can maintain stable forming accuracy, safe operation, and long-term productivity. Proper electrical maintenance not only strengthens performance but also prevents costly failures that interrupt the production schedule.
The following guide outlines key maintenance strategies to help ensure the electrical subsystem of your Metal Roof Machine stays in optimal condition.
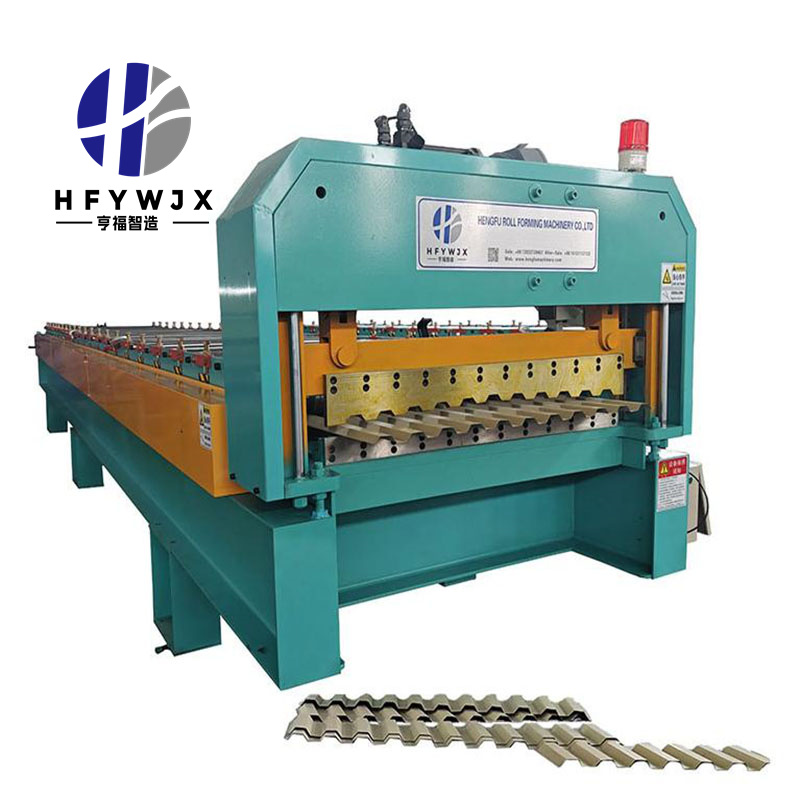
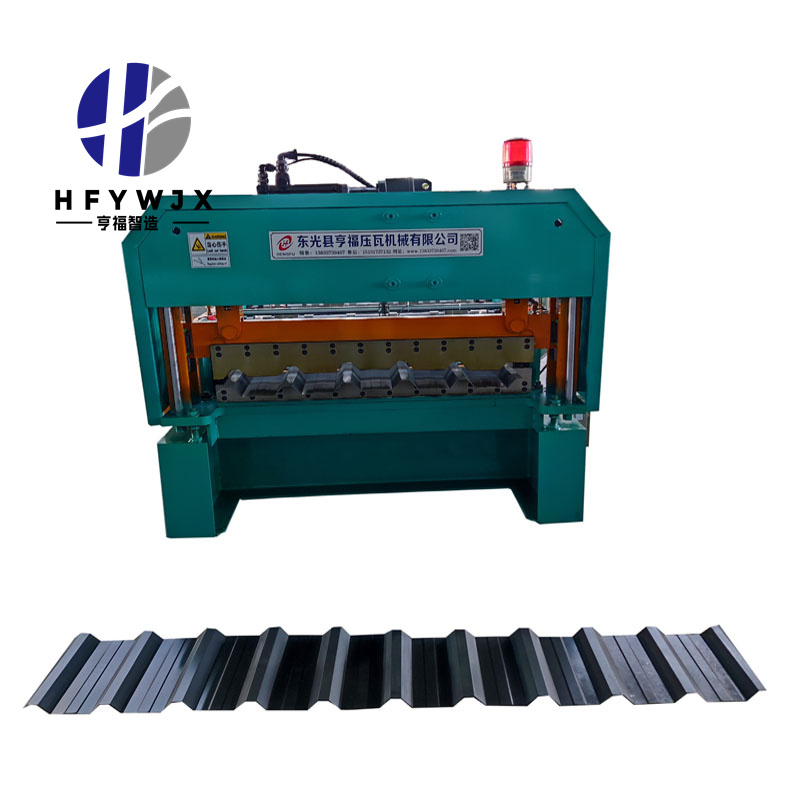


1. The Role of Electrical Maintenance in Metal Roof Forming
Electrical components manage nearly every functional segment of a Metal Roof Machine:
·Control logic, timing, and sequencing
·Speed regulation and motor performance
·Safety interlock operation
·Measurement and feedback signals
·Cutting precision and synchronization
·Trouble detection and fault shutdown
When one electrical module becomes unstable, the entire production line may experience length inaccuracies, inconsistent forming, overheating, or unplanned stoppage. Regular maintenance safeguards system reliability and keeps output quality consistent.
2. Build a Consistent Electrical Inspection Workflow
Successful maintenance begins with a structured routine. Creating a predictable inspection cycle ensures that issues are identified early, long before they disrupt production.
Daily inspection points
·Watch for abnormal indicator lights or warning messages
·Confirm all sensors detect movement and material properly
·Monitor startup and shutdown cycles for irregular behavior
·Listen for soft relay chatter or motor abnormalities
Weekly inspection points
·Examine cable lines for sharp bends, tension, or potential wear
·Check cooling fans and cabinet airflow
·Test the emergency stop circuits and safety-door switches
Monthly inspection points
·Open electrical cabinets to inspect internal components
·Remove dust, oil residue, and debris buildup
·Check terminal tightness and insulation integrity
·Examine grounding continuity
Such routines dramatically reduce the risk of electrical failure in a Metal Roof Machine.
3. Keep Electrical Cabinets Clean and Environmental Conditions Controlled
Inside the cabinet sits the most sensitive hardware:
·PLC control modules
·Servo and inverter drives
·Power-supply units
·Transformers and relays
·Contactors and fuses
Dust, humidity, and oil vapor are the biggest enemies of these electronics. To protect the system:
·Ensure cabinet doors seal properly
·Clean air filters and ventilation ducts
·Keep liquids and lubricants away from electrical enclosures
·Use cabinet dryers or heaters in damp climates
Keeping cabinets clean stabilizes component operation and prolongs circuit-board lifespan.
4. Tighten and Inspect All Wiring Connections
Metal forming naturally produces vibration. Over time, this vibration can loosen electrical connections, which may cause:
·Unstable power delivery
·Heat buildup at connection points
·Erratic sensor readings
·Intermittent drive or motor faults
·Random shutdown or restart cycles
During routine inspection:
·Tighten all terminals using a torque-calibrated tool
·Replace corroded or heat-darkened connectors
·Refresh aging insulation or wire jackets
·Ensure wiring loads match machine specifications
A secure wiring system ensures reliable and safe machine performance.
5. Maintain Sensors and Feedback Devices
Accurate measurement is vital for roof panel consistency. A Metal Roof Machine depends on various sensors to monitor position and material movement:
·Length-measurement encoder
·Proximity switches at key forming stages
·Safety-limit switches
·Position sensors for the cutter unit
Maintaining these sensors includes:
·Cleaning sensor faces with non-static cloth
·Realigning sensors to correct detection distance
·Checking output signals through the control panel
·Inspecting wiring for cracks or loose plugs
Sensor failures often show up as cutting errors or inconsistent panel lengths.
6. Monitor Motors and Drive Systems Carefully
Motors and electronic drives endure heavy workload, and their health directly affects production stability.
Motor maintenance
·Observe temperature levels during extended runs
·Ensure bearings operate smoothly
·Listen for unusual grinding or buzzing
·Confirm cooling fans operate correctly
Drive (inverter/servo) maintenance
·Review drive-error logs for early warning signs
·Clean dust off heat-dissipation surfaces
·Check input voltage and phase balance
·Back up drive parameters regularly
Well-maintained motors and drives support smooth sheet-feeding and forming control.
7. Protect PLC Hardware and Software Integrity
The PLC governs all machine logic, including forming order, sensor interpretation, motor timing, and emergency shutdown functions. Proper care ensures stable machine automation.
PLC maintenance should include:
·Creating backups of the control program
·Verifying tightness of I/O module contacts
·Cleaning modules with gentle compressed air
·Keeping the PLC protected from static discharge
·Using a UPS or stabilized power line
A stable PLC system guarantees predictable forming performance.
8. Guard Against Power Disturbances
Voltage fluctuations, surges, and grounding problems are frequent causes of electrical failures in industrial facilities. Protecting the power supply ensures:
·Smooth motor acceleration
·Error-free PLC processes
·Reduced stress on sensitive components
Use the following precautions:
·Install surge-protection devices
·Add industrial voltage regulators
·Ensure grounding resistance meets specifications
·Avoid connection to unstable or heavily shared circuits
Consistent voltage helps maintain long-term machine performance.
9. Check the Electrical Parts of the Cutting System
The cutter is one of the most electrically sensitive components in a Metal Roof Machine, requiring precise communication between sensors, drives, and control signals.
Regular checks should include:
·Testing sensor alignment for cut-cycle detection
·Inspecting solenoid valves on electrically-controlled hydraulic cutters
·Reviewing servo motor performance under load
·Checking wiring for vibration-related wear
Correct electrical calibration ensures accurate panel lengths without repeated manual adjustments.
Conclusion: Electrical Reliability Ensures Production Stability
A well-maintained Metal Roof Machine, delivered by a manufacturer with strong production capabilities and reliable bulk-supply support, can operate for many years with minimal interruption. By caring for the electrical system—cleaning cabinets, securing wiring, inspecting sensors, protecting drives, maintaining PLC performance, and stabilizing power sources—you ensure the machine remains accurate, safe, and highly productive.
When these maintenance practices become part of your regular workflow, you protect both the machine and your production efficiency, guaranteeing reliable output and long-term operational success.
References
GB/T 7714:Sheet metal forming: processes and applications[M]. ASM international, 2012.
MLA:Altan, Taylan, and A. Erman Tekkaya, eds. Sheet metal forming: processes and applications. ASM international, 2012.
APA:Altan, T., & Tekkaya, A. E. (Eds.). (2012). Sheet metal forming: processes and applications. ASM international.