Double Layer Roll Forming Machine Material Selection: Comparative Analysis of Steel vs Aluminum Alloy in Performance and Application
writer:优化 release time:2025-07-11 16:16:58 Views:96frequency
In industrial manufacturing, the double layer roll forming machine is a pivotal tool for processing sheet metal. The choice of roller material directly impacts the equipment’s operational lifespan, forming accuracy, and energy efficiency. This article provides a comparative analysis between steel and aluminum alloys, based on material mechanics, heat treatment techniques, and practical use cases, aiming to offer objective guidance for material selection in the roll forming industry.
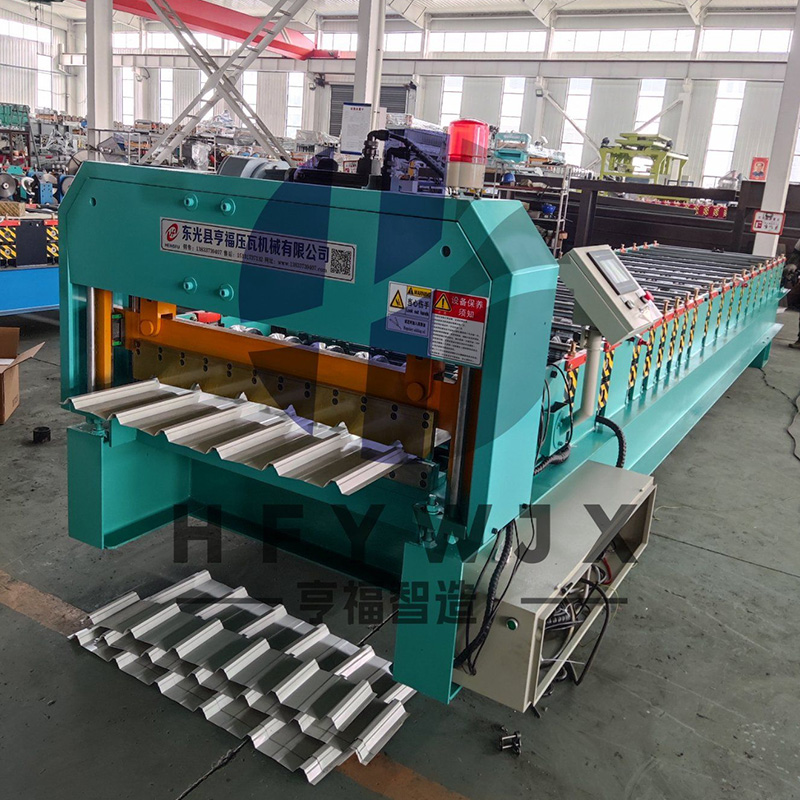


1. Steel Rollers: Balancing High Strength and Cost-Efficiency
1.1 Mechanical Performance Advantages
Steel, particularly high-strength alloy steels, is widely known for its superior tensile strength and impact resistance. According to research from Cranfield University, aluminum alloy 2219-T6 samples subjected to 45kN forming loads demonstrate tensile strength up to 450 MPa and yield strength around 305 MPa—highlighting the effectiveness of controlled forming under stress.
In roll forming operations involving thick or high-strength steel sheets, steel rollers deliver excellent durability under repeated deformation. Applications include automotive structural components, shipbuilding plates, and load-bearing frameworks.
1.2 Heat Treatment Optimization
Through tailored T6 treatment (solution hardening + artificial aging), steel rollers can achieve a refined microstructure, enhancing both toughness and precision. For instance, in aerospace-grade applications, heat-treated steel rollers have achieved machining accuracies down to 0.01 mm—critical for precision forming under high loads.
1.3 Economic Considerations
Steel typically costs 30%–40% less than aluminum alloys and is compatible with mature fabrication processes. In industries such as bulk materials transport and metallurgy, carbon steel rollers dominate over 80% of the market due to cost efficiency and availability.
2. Aluminum Alloy Rollers: Advancing Lightweighting and Corrosion Resistance
2.1 Lightweight Design
With a density roughly one-third of steel, aluminum alloys (e.g., 6063-T5) enable significant reductions in equipment weight and energy usage. Advanced modular conveyor systems using aluminum alloy rollers have achieved 40% weight reduction and up to 30% assembly efficiency improvement through standardized profile slotting designs.
This makes aluminum ideal for sectors with weight constraints, such as aerospace logistics or mobile processing units.
2.2 Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum forms a natural oxide layer, providing stable corrosion resistance even in humid or chemically active environments. In comparative salt spray tests (3.5% NaCl), 6063 alloy showed no visible corrosion after 240 hours, while untreated carbon steel developed rust within 48 hours—underscoring its advantages in pharmaceutical and food-grade systems.
2.3 Warm Hydroforming Capabilities
To address aluminum’s limited cold formability, warm hydroforming (controlled hydraulic bulging under elevated temperatures) allows complex part geometries with reduced thinning. Data shows that at 10 MPa chamber pressure and 4 MPa pre-expansion pressure, 6063-T5 alloy cylinder components achieved thinning ratios under 17.4%, compared to 30%+ in conventional cold stamping.


3. Material Selection by Industry Use Case
3.1 Heavy-Duty Forming
Recommended Material: High-strength steel (e.g., 2219-T6 equivalent)
Use Case: In marine applications, steel rollers are used for cold-forming steel sheets over 10 mm thick. Machines reach forming forces up to 2000 tons, with roller lifespans exceeding a decade.
3.2 High-Precision Manufacturing
Recommended Material: Aluminum alloy (6063-T5) with advanced thermal processing
Use Case: In 3C electronic casings, aluminum rollers enable ultra-thin wall forming (≤0.3 mm) with surface finish Ra ≤ 0.8 μm via hydroforming.
3.3 Corrosive Environments
Recommended Material: Aluminum alloy with anodic surface treatment
Use Case: Chemical conveyor systems benefit from aluminum rollers anodized for acid/alkaline resistance (pH 2–12), supporting service life over 15 years.
4. Emerging Trends: Composite Materials and Intelligent Processing
4.1 Hybrid Steel-Aluminum Rollers
Dual-layer roller structures are gaining traction. For example, a design combining an inner steel core for rigidity and an outer aluminum or thermoplastic (e.g., TPU) shell improves wear resistance. Hybrid rollers have demonstrated up to 25% weight savings and 15% cost reduction over all-steel designs, according to recent patent filings.
4.2 AI-Optimized Heat Treatment
Artificial intelligence is now being applied to heat treatment process optimization. Machine learning algorithms trained on over 2,000 datasets can now recommend optimized T6 cycles, reducing property variation from ±5% to ±1.5%, thereby improving batch consistency and machining precision.
Conclusion
The selection of roller material for double layer roll forming systems should be based on application-specific requirements:
For heavy-duty and precision forming: Steel rollers with refined heat treatments deliver unmatched performance.
For lightweight systems or corrosive environments: Aluminum alloys with thermal forming and protective coating offer superior benefits.
For budget-conscious applications: Steel remains the most economical solution without sacrificing structural integrity.
With the evolution of hybrid materials and AI-assisted processing, roll forming technology is entering a new era—combining strength, efficiency, and adaptability to support the future of advanced manufacturing.
References
Colegrove, P. A., et al. (2012). Layer-by-layer rolling for enhanced mechanical properties in MIG additive manufacturing. Cranfield University Technical Report.
SAE International. (2023). Aluminum Alloy 6063 Thermal Forming Guidelines, J2846.
MIT Mechanical Engineering Department. (2021). Steel Heat Treatment Optimization for Roll Forming Applications. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 15(2), 88–95.